Contact Info
- 022 - 62597830
- 022 - 62597837
- info@breachcandyhospital.org
- Ground Floor, Breach Candy Hospital Trust 60 A Bhulabhai Desai Road, Mumbai-400026.
Interventional Radiology
Interventional Radiology is a branch of medicine which is devoted to treating various vascular (other than the heart) and non-vascular conditions, through integration of clinical and imaging based diagnosis and minimally invasive therapy. These procedures are performed by trained Interventional Radiologists.
Interventional radiologists are doctors who with the help of mainly specialized X-ray machines, use their expertise to guide tiny instruments, such as catheters, through blood vessels or through the skin to treat various diseases without surgery.
Interventional radiologists are specialists who have trained rigorously in minimally invasive interventions using imaging guidance; they combine their imaging background with clinical knowledge to treat various vascular and non-vascular pathologies.
With their expertise in imaging and the specialized and advanced training only in the field of non-surgical techniques with imaging guidance, interventional radiologists can treat a large number of ailments within the body by delivering the treatment directly to the source of the problem.
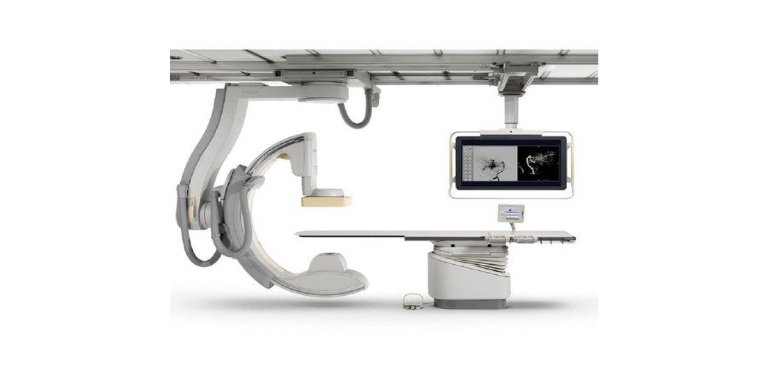
Breach Candy Hospital has a state of the art Interventional radiology suite. The Philips Allura Clarity FD 10 has high resolution digital subtraction images, with low radiation. Adjunctive machines such as peripheral laser, intravascular ultrasound, doppler are part of the department and greatly enhance the procedural results.
With the availability of the best imaging modalities (USG, CT, MRI, PET scan) and highlyt trained Interventional Radiologists (IR’s), the interventional radiology unit of Breach candy is one the best in the country.









